By Sumaiya Farheen, January 2024.

Groin strain can be a debilitating and frustrating injury, often caused by sudden movements or excessive stress on the muscles in the groin area.
In this blog, we will explore some of the most effective non-invasive treatment options for groin strain.
What does a groin strain feel like?
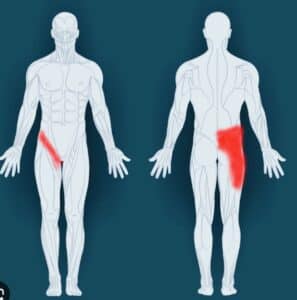
A groin strain refers to an injury or strain to the muscles located in the inner thigh area where the thigh connects to the pelvis. The severity of a groin strain can vary, ranging from mild to severe, and the symptoms can differ depending on the extent of the injury.
What is A Grade 1 Groin Strain Recovery Time?
The recovery time for a grade 1 groin strain can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the injury. Though, typically as a grade 1 groin strain involves minimal tearing of the groin muscle, 1-2 weeks may be an adequate healing time before resuming activity. Read our blog for more insight into muscle strain recovery.

The initial phase of recovery involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to reduce pain and inflammation. Throughout this period, it is crucial to steer clear of activities that might exacerbate the injury and to provide the muscles with the necessary time to heal.
NHS Groin Strain Exercises
As you recover from a groin strain, it’s crucial to rest, permit the injury to heal, and gradually reintroduce exercises to strengthen the muscles.
Here are a few exercises that can aid in the recovery process-

*Gentle Stretching- Enhance flexibility and alleviate muscle tightness in the groin area with gentle stretches. Sit on the floor, legs extended, and bring the soles of your feet together. Slowly push your knees toward the floor, feeling a stretch. Hold for 20-30 seconds, repeating several times.

*Isometric Contractions- Strengthen injured muscles with isometric exercises. Lie on your back, knees bent, and feet flat. Place a ball or pillow between your knees and squeeze them together against resistance. Hold for 5-10 seconds, release, and repeat 10-15 times.
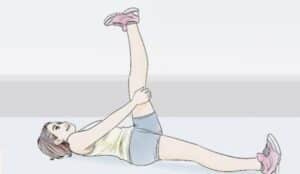
*Straight Leg Raise- Lie on your back, one leg straight, and the other bent. Engage your core, lift the straight leg toward the ceiling, and lower it slowly. Begin with 10 repetitions per leg, increasing gradually.
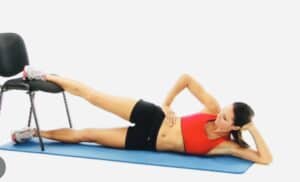
*Side-lying Leg Lift- Lie on your side with the injured leg on top. Keep the bottom leg slightly bent. Lift the top leg toward the ceiling, emphasizing control. This exercise aids in strengthening and toning.
Groin Strain NHS Treatment
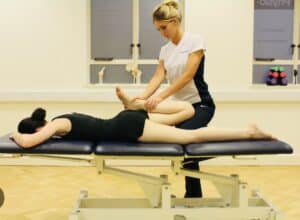
*Massage Therapy-
A holistic approach targeting soft tissues.
Improves blood flow, reduces tension, and aids healing.
Skilled therapists use techniques like myofascial release for pain relief.
Regular sessions contribute to faster recovery and injury prevention.
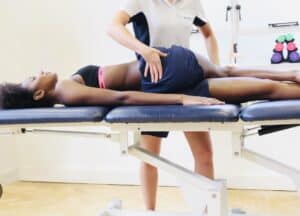
*Osteopathy-
Focuses on body structure and function relationship.
Hands-on techniques aim to restore balance and enhance self-healing.
Involves gentle joint mobilizations, stretching, and soft tissue manipulation.
Non-invasive techniques address imbalances and promote recovery.

*Physiotherapy-
Crucial for groin strain rehabilitation.
Therapists assess, create personalized plans, and guide exercises for healing.
Modalities like ultrasound and electrical stimulation reduce pain and inflammation.
Aims to restore function, improve mobility, and prevent recurrences.

*Chiropractic Care-
To initiate the hip adductor stretch, position yourself by standing with your feet positioned wider than shoulder-width apart. Chiropractors may use soft tissue techniques and rehabilitative exercises for support.
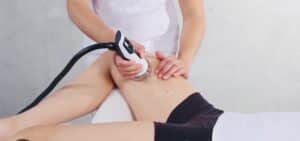
*Shockwave Therapy-
Non-invasive procedure utilizing high-energy sound waves.
Beneficial for chronic or stubborn groin strains.
Promotes blood flow, accelerates tissue repair, and reduces pain.
Administered over several sessions, showing promising results in symptom relief.
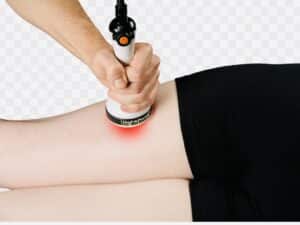
*Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)-
Uses low-intensity lasers to stimulate cellular healing.
Reduces pain, inflammation, and promotes tissue repair.
Gaining popularity in sports medicine, showing promise in treating groin strains.
Conclusion
In the realm of treating groin strains, non-invasive options can prove effective in promoting recovery and restoring function.

The choice of treatment depends on individual preferences, severity of the strain, and recommendations from healthcare professionals. Consider consulting with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable non-invasive treatment option that aligns with your needs and goals for a swift and successful recovery.
